How to Become a Digital Markeert: A Guide to Career Options & Salaries

Digital marketers blend their technical savvy and creative passion into one of the most rewarding — and growing — professions in the online world. Pursuing a digital marketing career can be overwhelming, but the chances are that the upskilling process won’t be as hard as you think. In fact, you probably already possess some of the skills required to get started!
Here’s a guide on how to become a digital marketer, even if you have no formal experience in the field.
6 Steps to Becoming a Digital Marketer
Do you love social media, know how to spot an influencer, and have a flair for writing? If so, you’re off to a good start! Below, we’ve listed the six steps that digitally savvy professionals will need to take to become fully fledged digital marketers.
1. Assess Your Current Skill Set
You might not have held a job with “marketing” in the title before, but that doesn’t necessarily mean you lack career-relevant experience. Countless career paths converge into the digital marketing space; professionals who have experience in advertising or customer service are excellent marketing candidates, as are skilled communicators. In fact, aspiring digital marketers can readily transition from careers in sales, marketing, communications, web design, or even data analytics.
Here’s a quick list of the core capabilities you’ll need to develop as you figure out your digital marketing career options:
- Brand development
- Competitive research
- Content strategy
- Conversion tactics
- Paid search
- Customer service
- Social media management
Take a good, long look at your resume. Which relevant professional marketing skills do you have — and which do you still need to accrue?
2. Gain a Foundational Understanding of Digital Marketing
Advertising and branding are at the core of digital and old-school commerce alike. However, selling in the digital world is even more competitive; personal, corporate, and nonprofit brands compete for attention across countless buying platforms. Digital marketers need to propel their clients’ brands above the competition with audience-attuned, engaging, and timely advertising content.
But a good digital marketer’s work goes beyond developing successful advertising campaigns. These branding professionals position companies and services prominently and positively in online search engines and through social media strategy. They reach niche demographics on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok by producing compelling multimedia content and stories. In some cases, they may also work with influencers to bolster a brand’s visibility among its target audiences.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of what digital marketers do, let’s address how to become a digital marketer and find your first job.
3. Obtain an Education
There are several educational routes into digital marketing, here are some of the primary options: degree programs, bootcamps, or self-directed study. All three offer unique learning experiences and require different investments of time and money.
Not sure which is the best for you? Let’s walk through the pros and cons of each.
Bootcamp Learning
A digital marketing bootcamp is an 18-week, multidisciplinary course that provides opportunities for hands-on learning. The online curriculum leads participants to become proficient in digital advertising, marketing strategy, and website analytics.
Most bootcamp curricula cover topics such as targeting and building audiences, brand strategy, and search engine optimization (SEO). Upon completing the bootcamp, learners will be able to design their own digital marketing strategy — and have a strong portfolio of work to show to future employers.
With an online curriculum, bootcamps also typically offer flexible schedules. Further, they require no previous marketing or programming experience. To sum up, if you’re willing to put in the hard work, bootcamps can be an effective means of gaining the foundational skills you need to prepare to launch your digital marketing career.
Degree Programs
If you want a deep dive into the theory and practice of PR, advertising, and brand marketing, a four-year college program might be your best bet. Obtaining a degree in advertising, marketing, journalism, or design can prepare you for an entry-level digital marketing role.
Even having a seemingly unrelated major like computer science or data analysis can be helpful — after all, today’s marketers are more reliant on digital platforms and analytical tools than they have ever been in the past.
That said, if you have an undergraduate degree in a field that doesn’t lend itself as easily to digital marketing, you may want to consider enrolling in a master’s degree program. Advanced degree programs often explore analytics, design, or global marketing, all of which are invaluable to aspiring professionals.
Degree programs are valuable in their comprehensiveness; however, they may not be the best answer for everyone wondering how to become a digital marketer. By definition, degrees require multiple years of full-time study and tend to be expensive. However, if you have the time, money, and inclination to invest in a degree, you’ll be well-positioned for a career in digital marketing by the time you complete your studies.
Self-Directed Study
Perhaps you want to explore specific digital marketing specialties but don’t have the time or inclination to pursue a formal education. If so, self-directed learning might be your best bet. These days, online digital marketing courses offer a comprehensive dive into marketing principles. You can study analytics, copywriting, and social media management, as well as content and email marketing. All are valuable topics for aspiring marketing professionals to cover.
That said, a self-directed approach isn’t always the easiest to adopt. Those who try to learn independently need to be highly motivated self-starters who don’t need an instructor or formal class time to motivate their learning. Consider your learning style before you start! If you think you can keep yourself on track, try self-directed learning. But if you need a classroom environment to thrive academically, you may want to consider a bootcamp or college course.
4. Get Real-World Practice
If you want to land a job in digital marketing, you’ll need to develop a portfolio — that is, a curated collection of projects that demonstrates your technical marketing skills to prospective employers.
Those who attend college programs or bootcamps can accrue portfolio projects through their coursework; capstone projects are often designed for that very purpose. However, aspiring digital marketers aren’t limited to developing their portfolios in class.
As another example, internships offer an entry point into a digital marketing career, giving you the opportunity to craft a website or digital advertising campaign for a real-world brand. This work, of course, can also be shown to prospective employers during your future job searches.
Digital marketing also rewards self-starters. A new college alumni or bootcamp learner can bolster their portfolio and resume by volunteering at organizations that don’t have the budget for paid internships or freelancers. Maybe you know a community nonprofit that could benefit from a savvy social media campaign; or perhaps a startup business in your town needs a signal boost to build its identity. In either case, helping them helps you!
Submit a proposal to one of these small organizations outlining how your skills and expertise could boost their brand visibility. Include the broad strokes of what your proposed campaign would look like. Even if the work is unpaid, you’ll gain valuable experience and references.
Additional Resources:
- 7 Tips to Help Land That Internship — Investopedia
- The Ultimate Guide to Freelancing — Hubspot
- 3 Volunteer Opportunities That Will Seriously Boost Your Career — The Muse
5. Build a Professional Network
Growing a robust professional network is key to building a professional career. Connections can help you stay in tune with industry news, get word of new digital marketing career options, and gain valuable insights on industry advancements.
Not sure how to get started? Consider attending professional workshops or digital marketing seminars. Many are conducted online, offering expert insight and opportunities to meet industry leaders.
Remember that your professional brand is integral to networking. Even if you prefer keeping your personal accounts on social media private, a public-facing professional account can help you get attention. It also offers proof of your digital marketing skills.
Getting creative on social media can be beneficial, too. Start or contribute to a newsletter about digital marketing — launch a blog if you have time! Establish yourself as an authoritative presence in marketing groups and message boards. The more you can build an online reputation that telegraphs your marketing skills and savvy, the better off you’ll be in the interview room.
6. Apply to Jobs
Searching for jobs is always stressful — but with a bit of organization and preparation, you can dial back that anxiety.
First, develop your application materials. You need to have a knockout resume that clearly telegraphs your skills, education, and professional achievements. As mentioned earlier, you should also have a portfolio that illustrates the capabilities you list in your resume via real-world projects.
Once you have your materials handy, you can start applying to jobs. Check out job boards like Indeed and Monster, as well as professional platforms like LinkedIn. Once you’ve found a few positions you think would be a good fit, start applying! Record your application statuses in a spreadsheet or other document so you can easily keep track of pending communications and interviews.
If you’re applying for a digital marketing job, know your skills, what skills specific employers require, and how to bridge those needs. Research a company’s mission, product line, and audience when you apply — employers like applicants who have done their homework!
Next, tailor your resume and cover letter to the organizations or companies you’re applying to. Be direct, be patient, and, most of all, be positive. You never know when or from where an opportunity might develop.
Additional Resources:
- How to Write a Compelling Marketing Resume — The Muse
- How to Create a Marketing Portfolio: Tips and Examples — Wix
- Marketing Job Interview Questions and Tips — The Balance Careers
Top 7 Career Options in Digital Marketing
As you determine your path to becoming a digital marketing specialist, you’ll need to figure out your general career direction. After all, digital marketing is an umbrella term that encompasses a variety of subfields. Let’s highlight a few!
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
A slick website that offers exciting products or services is useless if people can’t find it. Companies want their sites at the forefront of online searches. Search engine optimization (SEO) makes that happen.
A successful SEO strategy places sites in front of people more quickly, builds web traffic, and raises sites’ value. Understanding the importance of SEO is easy — but because best practices evolve constantly, the specialty requires continuing education and training.
Those who deliver strong SEO results know how to combine exciting content with the right search keywords, clear titles, and meta information that make their pages quick and easy to find. A good SEO strategist blends science and instinct to determine what customers are searching for and how to make their websites stand out online.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC)
Paid online advertising can be a confusing warren of rates, scores, and strategies. But it’s important to understand the broad strokes of how pay-per-click advertising works.
With pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, digital marketers essentially place display ads in search engines. The advertiser pays only when an online user clicks on the ads.
Pay-per-click marketing is essential for marketers attempting to promote specific brand names. Notice the word “ad” displayed next to a link when you search for, say, a hotel brand or shoe manufacturer? That’s pay-per-click advertising.
By using such advertising, digital marketers can take advantage of specific keyword searches to drive their sites to the top of search engines. If done well, pay-per-click marketing can be an invaluable part of an overarching campaign.
CRO
Conversion rate optimization (CRO) is designed to turn web traffic into action. A conversion rate represents the percentage of visitors to a site who perform a task while there. These visitors become “converts.”
Tasks can include filling out a survey, registering for a newsletter, or buying something. By converting visitors on your website, you create the chance to close a sale or, even better, generate direct revenue for the business. Digital marketers skilled in this field know how to optimize sites to encourage viewership and buying decisions.
Social Media Marketing
Any company or organization looking to connect with people must have a compelling social media strategy. It’s not enough simply to operate accounts on Facebook, Twitter, or Instagram; sound social media marketing requires deft touches for sales, public relations, and audience engagement. A sense of humor doesn’t hurt, either.
According to Statista, about 4.4 billion people worldwide are expected to use social media by 2025, making it a promising — if sometimes overwhelming — avenue for brand promotion.
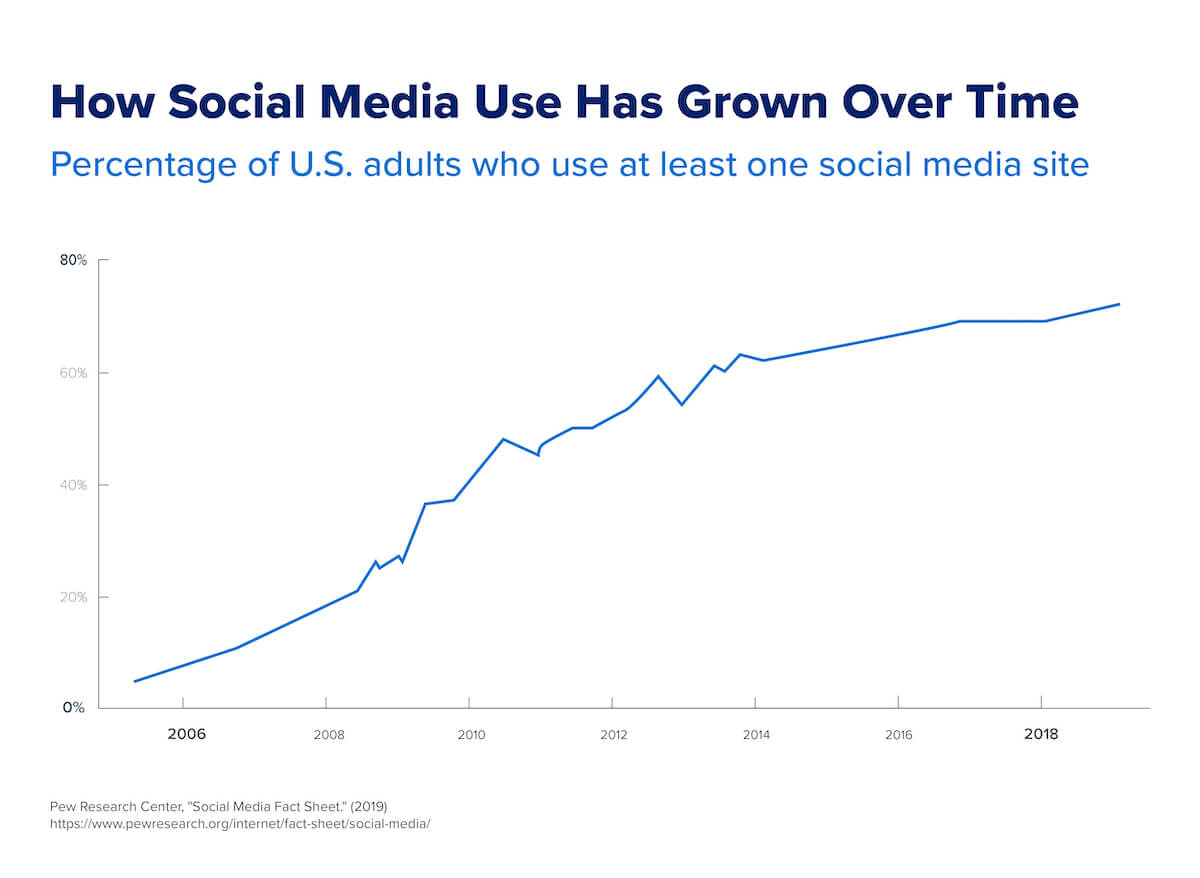
Good social media marketers understand how engaging, entertaining, and quirky content can attract eyes and spread brand messaging through shares. They can also tailor their approach by assessing their competitors’ social media successes and faux pas. By knowing where audiences congregate, when they visit, and what compels them to react, successful social media marketers can deliver a host of fresh promotional opportunities on high-potential social platforms.
Email Marketing
Sound old-school? It might be. Yet, email marketing remains an important sales driver — one that, when used effectively, can lead to better engagement with your target audience.
Yes, email marketing has developed a negative reputation because of spam blasts and phishing scams. But when used effectively, email marketing offers a fine way to forge personalized relationships with clients and customers. It can be successful, too; about two-thirds of customers report having bought something through email marketing.
Further, email continues to be the preferred method of communication among professionals. For business-to-business marketing campaigns, email is a worthwhile (and cost-effective) approach.
Content Marketing
Content marketing’s history predates the internet. Those in the right demographic remember department store catalogs that weighed several pounds and highlighted thousands of products or comic books that used stories to boost action figure sales.
At its heart, content marketing is about storytelling. In whatever medium, it delivers your story to potential consumers. A comprehensive content marketing strategy considers the product, the audience, and the best places to put them together. As an online content marketer, you can create campaigns to sell an idea rather than a product or service.
Influencer Marketing
Not long ago, the primary influencers — those hired to sell products — were actors, athletes, and musicians. Today, social media has produced a new generation of influencers, people who have branded themselves online and can leverage the attention they receive into lucrative endorsements. Some develop huge audiences with glamour shots from exotic locations; others grow their popularity by crafting a more authentic, down-to-earth feel.
With influencer marketing, you look for Instagram or TikTok stars who have followings to which your campaign might appeal. You might deal with influencers with several million followers or “micro-influencers” whose several thousand followers form a small, if promising, niche. Having strong digital communication skills and budgeting savvy is key to this marketing subfield.
Skills You Need to Become a Digital Marketer
Good digital marketers understand brand management, content strategy, and search engine optimization. They are salespeople and storytellers; these strategic professionals can set long-term project goals and adjust them to suit the digital world’s real-time whims.
Essential digital marketing skills include knowledge of SEO, data analysis, competitive research, and content strategy. Content marketing, or the storytelling element of any good marketing strategy, should also be an essential part of your curriculum.
As for soft skills, digital marketers should be persuasive communicators with a sense of curiosity and empathy. Try to understand what your customers want before developing a digital marketing strategy to sell it to them!
What Tools Do Digital Marketers Use?
Digital marketers have plenty of tools at their disposal. Some are universal, such as Google Analytics. As perhaps the most used analytics tool, Google Analytics shows who is visiting your website, where they were referred from, and which pages draw the most attention. It’s a must-use for digital marketing professionals.
Google Ads and Facebook Ads Manager are popular options for buying ad space on their respective platforms. A tool such as MailChimp can be vital for putting together email marketing campaigns. For SEO solutions, tools such as BrightEdge and Screaming Frog provide clean recommendations and research to help users understand and capitalize on customer searches.
Career Paths in Digital Marketing
Wondering where a digital marketing career path might take you? Here are a few common entry-level roles to consider once you complete your education and begin your job search.
- Social Media Strategist: As their titles suggest, social media strategists are responsible for developing, posting, and otherwise managing all content that appears on a company’s Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, or other social media feeds. They may also take on responding to consumer messages, assessing profile metrics, and developing social outreach strategies.
- Digital Marketing Associate: Digital marketing associates are entry-level marketing generalists. They often manage a client’s websites, social media platforms, paid spends, and email marketing campaigns. They may contribute to the development of a brand’s overarching marketing strategy.
- Content Writer: Content writers develop blogs, social posts, website landing pages, and other copy for their clients. These professionals tend to be specific in their roles; while they may have input into content-based strategy sessions, they typically have fewer contributions to social media and other marketing channels.
How to Get an Entry-Level Digital Marketing Job
The digital marketing funnel is wide. Copywriters, salespeople, designers, and video editors can all find their way into the field with relative ease. That said, landing an entry-level digital marketing job takes patience and persistence.
If you’re not getting any hits after filing job applications, try finding other ways to establish yourself in the field and gain some industry experience. You can thrive with some personal ingenuity; start a blog, newsletter, or website of your own. Offer freelance help designing a website for a local nonprofit or startup. Begin podcasting. Try things to get yourself — and your work — seen and heard! In time, you’ll connect with an employer who appreciates your skills.
(For more basic application advice, see our above section on applying to jobs!)
Digital Marketing Certifications
Certification courses cover a lot of ground in a short time, allowing you to craft an online course of study at your own pace. A certification course in digital marketing can be handy for professionals seeking to branch out or just learn more about the field. Courses are conducted online, last about three months, and distill core topics into a series of lectures and real-world applications.
Need some tips on where to look? Here are a few certification courses that aspiring digital marketers might find helpful.
Additional Resources:
- Social Marketing Certification Course — Hootsuite
- About the Google Ads Certification — Google Support
- Certifications — Hubspot Academy
How Much Do Digital Marketers Make? Job Outlook and Salaries
Career opportunities in digital marketing abound and are projected to keep growing. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for marketing managers will grow seven percent by 2029. That outpaces the national rate of job growth, which is four percent. In New York state, job prospects are expected to grow at an even faster pace: CareerOneStop predicts the number of jobs for marketing strategists to grow 26 percent by 2026.
“Advertising, promotions, and marketing manager positions are highly desirable and are often sought by other managers and experienced professionals. With Internet-based advertising becoming more important, advertising managers who can navigate the digital world should have the best prospects,” the Bureau of Labor Statistics states.
Further, digital marketing salary prospects are promising as well. According to recent wage data, the median pay for digital marketing specialists was $72,750. A number of factors influence salary, including company size and industry, as well as a candidate’s experience and knowledge of in-demand skills.
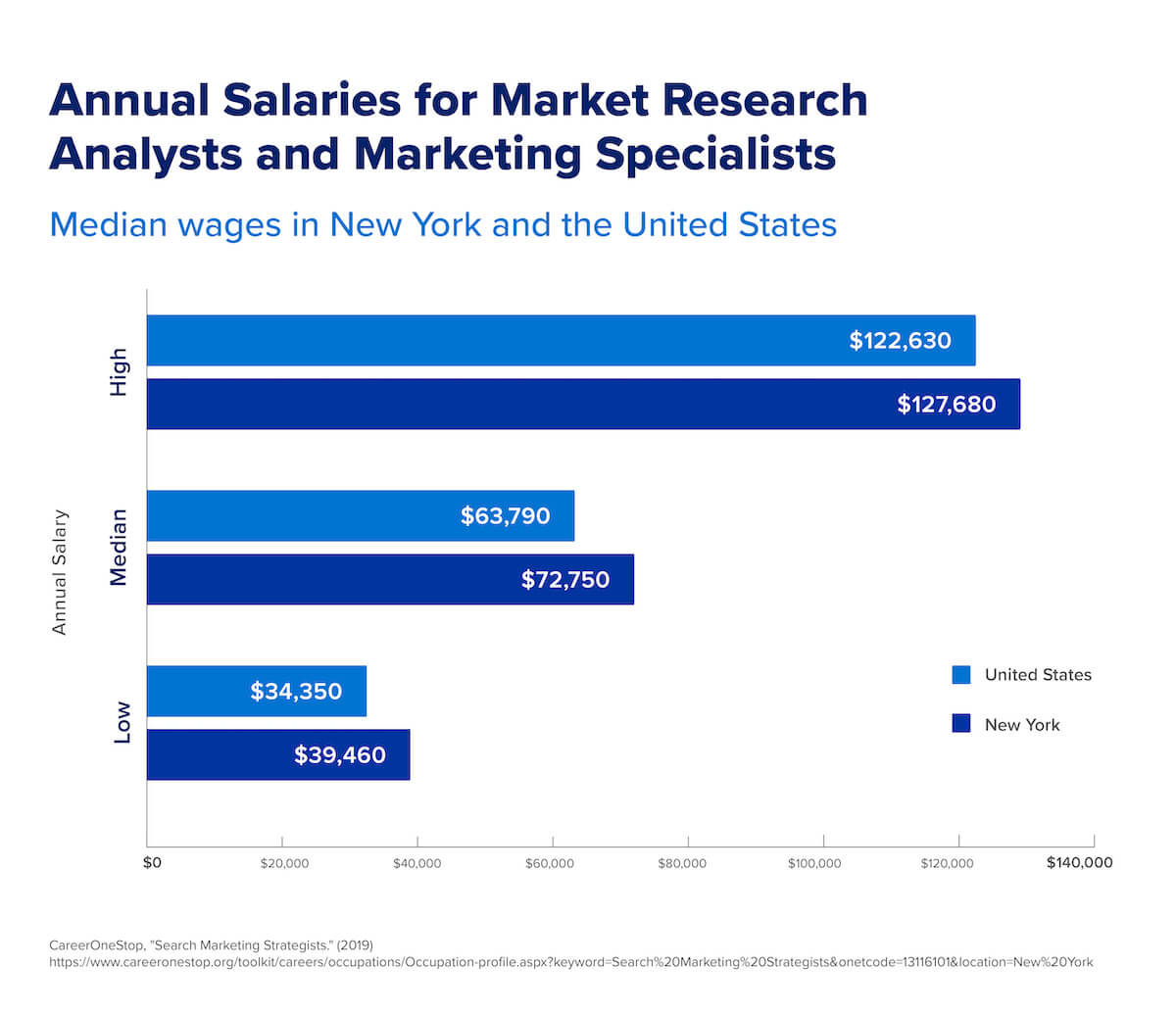
Of course, the trend toward remote work has broadened the job-searching net. That means that even if you live in another state, you may be able to land a high-paying digital marketing job in New York City.
Should You Become a Digital Marketer?
Digital marketing is a fast-paced, growing field that rewards those with multiple skill sets. It requires technical skills, creativity, and a passion for combining the two.
Digital marketing also offers the opportunity to find good-paying jobs for a variety of industries. Organizations in finance, healthcare, education, and sports all seek talented digital marketing specialists.
If you’re considering the field, Columbia Engineering Digital Marketing Boot Camp is a great place to start. In 18 weeks, you will learn the core proficiencies of digital marketing, gain experience with the leading trade tools, and apply your skills to real-world projects. Moreover, because the bootcamp is conducted online, your chosen curriculum can fit flexibly within your existing schedule.
Reach out today to see if Columbia Engineering Digital Marketing Boot Camp might be a good fit for your career goals!
.png)




